
Background
As droughts and increasing populations dwindle freshwater supplies in semi-arid regions like Southern California, water districts depend more on advanced water reuse technologies to convert wastewater into safe potable water. Orange County Water District’s Groundwater Replenishment System (OCWD GWRS) is currently the world’s largest indirect potable reuse facility. Producing a total of 378 million liters per day (100 MGD), with an additional 114 MLD (30 MGD) planned for completion in 2023, the facility is a benchmark in advanced wastewater purification. The treated water serves two functions by recharging a groundwater aquifer to increase the drinking water supply and injected into wells to create a seawater intrusion barrier. Qualification as a membrane supplier at GWRS requires up to 10,000 hours of membrane piloting and evaluation of specific flux, permeate quality, and resilience to chemical cleaning.
Qualification
LG BW 400 ES, LG Chem’s energy-saving RO membrane, was piloted in the first stage of a full-scale RO train at
GWRS with the operating conditions and requirements for qualification listed below:
Operating Conditions:
- Flux: 25.3 lmh (14.9 gfd)
- Recovery rate: 55%
- Temperature range: 23–30 °C (73–86 °F)
Performance Criteria:
- Two CIP’s consisting of one aggressive and one standard
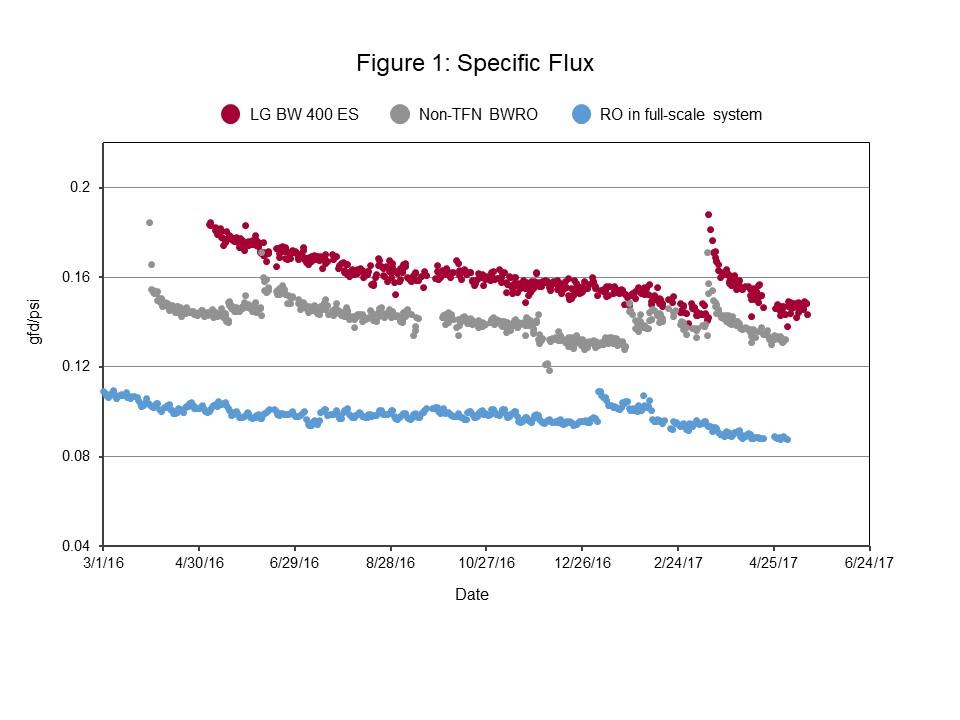
- Specific flux >21.2 lmh/bar (0.085 gfd/psi)
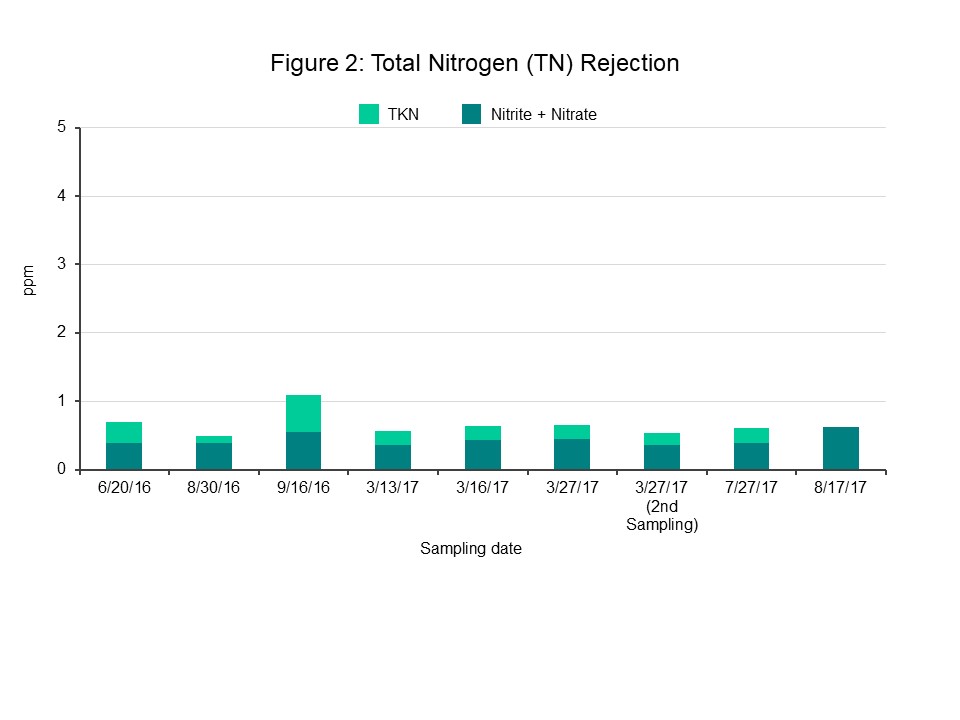
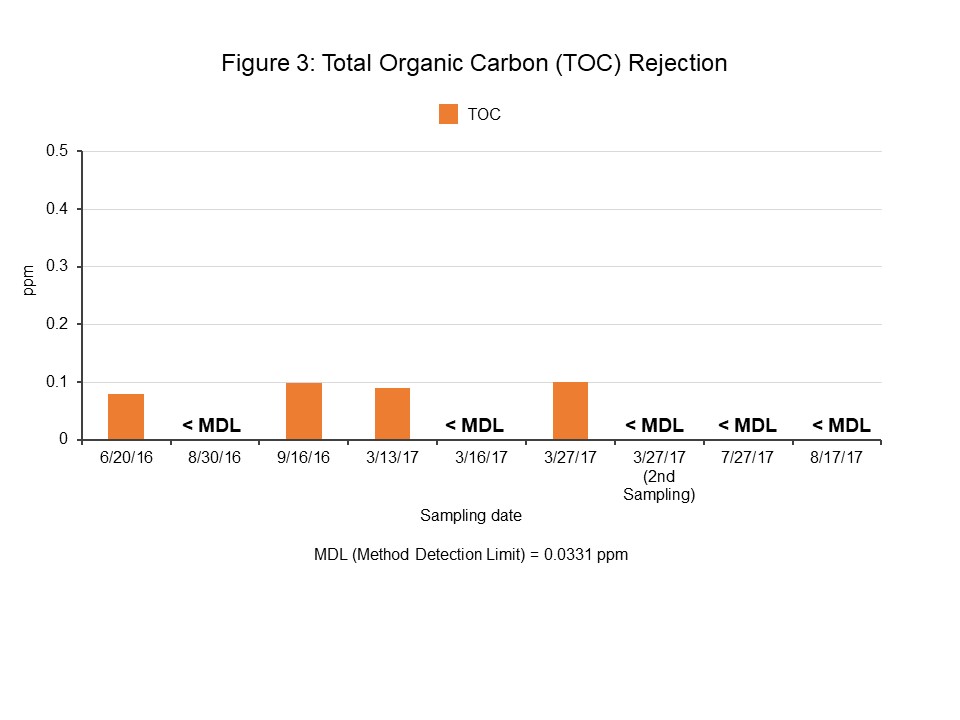
- TDS <30 mg/L, TOC <0.1 mg/L, Total Nitrogen < 5 mg/L
Results
LG BW 400 ES demonstrated strong performance during the qualification phase that lasted more than a year. The following are some key advantages observed through the pilot study:
- Low Energy Consumption: LG BW 400 ES yielded the highest specific flux among all membranes tested at GWRS for excellent energy savings (see Figure 1)
- Outstanding Nitrogen & Organic Removal: TN and TOC reduced to concentrations substantially lower than the maximum acceptable levels (see Figures 2 and 3).
Outcome
Following the successful qualification trial, LG Chem was awarded the opportunity to replace three trains at GWRS, totaling 57 MLD (15 MGD). LG NanoH₂O™ RO membranes continue to perform reliably and exemplify the robustness of LG Chem’s Thin-Film Nanocomposite (TFN) membrane technology for wastewater reuse applications.